Remote Sensing for Precision Agriculture


What is Remote Sensing?
Remote sensing is primarily concerned with collecting and interpreting information about an object or landscape from a remote vantage point. Examples of remote sensing include aerial photography, satellite imagery, radar altimetry and laser bathymetry. Coupled with ground measurements, remote sensing can provide valuable information about the surface of the land, the oceans and the atmosphere. Remote sensing makes use of visible, near infrared and short-wave infrared sensors to form images of the earth's surface by detecting the solar radiaton reflected from targests on the ground.
Energy interactions with the earth's surface & atmosphere:
-
Reflection (albedo)
-
Absorption (change light energy into heat energy)
-
Refraction (bending of light energy)
-
Transmission (passage of energy through a medium)
-
Scatter (diffusion of radiation by particles)
There are two main types of sensors:
-
Active sensors - emits energy in order to scan objects and areas whereupon a sensor then detects and measures the radiation that is reflected from the target.
-
Passive sensors - detect natural radiation that emitted or reflected by the object or surrounding areas. Reflected sunlight is the most common source of radiation measured by passive sensors.

Electromagentic Spectrum
Remote sensors have been refined over the past several decades to cover the visible, reflected infrared, thermal infrared, and microwave regions of the spectrum.
Platforms and Sensors

Sattelite - Landsat 8
DA42 Aircraft

Remote Sensing Backround
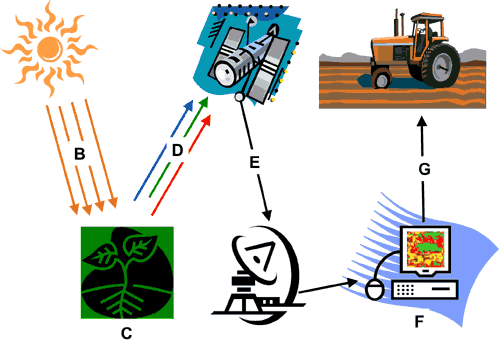
Remote Sensing Process
The sun (A) emits electromagnetic energy (B) to plants (C). A portion of the electromagnetic energy is transmitted through the leaves. The sensor on the satellite detects the reflected energy (D). The data is then transmitted to the ground station (E). The data is analyzed (F) and displayed on field maps (G).